Electrically conductive/dissipative packaging

Electrically conductive or dissipative packaging is especially used in areas where there is a risk of explosion and fire. The discharging properties of the packaging prevent static charging of the products and, thus, contribute to explosion protection.
What does “electrostatic discharge” mean?
What are “electrostatic propeties”? What is “surface resistivity”?
What is the difference between electrically insulating, dissipative and conductive?
How do plastics become dissipative or conductive?
For what purposes is electrically dissipative or conductive packaging used?
How is electrically dissipative or conductive packaging marked?
How is packaging tested for electrostatic properties? Which testing methods exist?
What is provided for under the ATEX directive?
What is regulated in the ATEX Product Directive no. 2014/34/EU?
What is regulated in the ATEX Operating Directive no. 1999/92/EC?
What is regulated under VEXAT?
What relevance do the ATEX and VEXAT directives have for packaging?
What does “electrostatic discharge” mean?
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) results in electrical breakdowns due to potential differences which may be visible as sparks. During electrical breakdowns, a high level of electric current is created for a short period.
Damage to electrical components can be caused during electrostatic discharge. In addition, the discharge may pose a risk of fire and explosion. Flammable substances might ignite or explode due to the high level of electric current during discharge.
What are “electrostatic properties”? What is “surface resistivity”?
Electrostatic properties are defined by surface resistivity. Depending on this, a material or substance is described as being electrically insulating, dissipative or conductive.
Dissipative or conductive materials ensure that existing electrical charges are slowly discharged and that the risk of explosion and fire from hazardous substances is reduced.
Surface resistivity
This term refers to the ability to resist surface current flowing across the material surface. Surface resistivity is indicated in ohms. Depending on the level of surface resistivity, a material is deemed insulating, dissipative or conductive. Surface resistivity depends on the material and is also strongly influenced by external factors. Both humidity and the ambient temperature affect the electrostatic properties of a material.
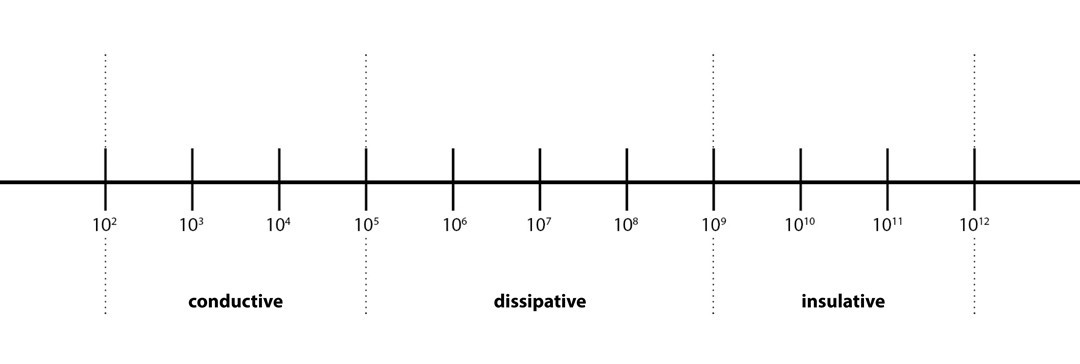
What is the difference between electrically insulating, dissipative and conductive?
Insulating
Materials with a surface resistivity of 109–1012 ohms are deemed insulating.
Dissipative
Dissipative materials have a higher electrical resistivity than conductive materials. These materials have a surface resistivity between 105 –109 ohms.
Conductive
When surface resistivity ranges between 102–105 ohms, materials are said to be electrically conductive.
How do plastics become dissipative or conductive?
Plastics are basically insulating. Various substances can be added to make a plastic dissipative or conductive.
Usually, chemical additives, carbon fibres or sooty particles are added to the plastics.
For what purposes is electrically dissipative or conductive packaging used?
Electrically dissipative packaging is used whenever static charges and associated electrostatic discharges are to be avoided.
Conductivity of packaging is important when handling sensitive electronic components. Dissipative packaging is also used in the chemical industry when filling substances with a risk of explosion or fire.
How is packaging tested for electrostatic properties? Which testing methods exist?
There are various test methods regarding electrostatic properties of packaging. At FRIES, we mainly use ring electrode tests, surface measuring devices and measurements by means of high voltage.
What is provided for under the ATEX directive?
The ATEX is an EU Directive, with “ATEX” meaning “Atmosphères Explosibles”. The ATEX Directive is subject to two separate Directives: the ATEX Product Directive no. 2014/34/EU and the ATEX Operating Directive no. 1999/92/EC.
ATEX regulates equipment and protective systems in potentially explosive atmospheres and is aimed at all EU member states.
What is regulated in the ATEX Product Directive no. 2014/34/EU?
The ATEX Product Directive 2014/34/EU sets out the rules which apply to products and equipment used in potentially explosive atmospheres. The aim of the Directive is to protect individuals working in potentially explosive atmospheres.
The Regulation defines various device groups. Each device group has different requirements and hazards.
Group I
Equipment for mining, surface and underground operations
Group II
Equipment for potentially explosive dust or gas atmospheres
Group III
Equipment for potentially explosive dust atmospheres
What is regulated in the ATEX Operating Directive no. 1999/92/EC?
The ATEX Operating Directive no. 1999/92/EC is often referred to as “ATEX 137”. This Directive defines the safety requirements for personnel working in potentially explosive atmospheres. The aim is to improve health protection of employees.
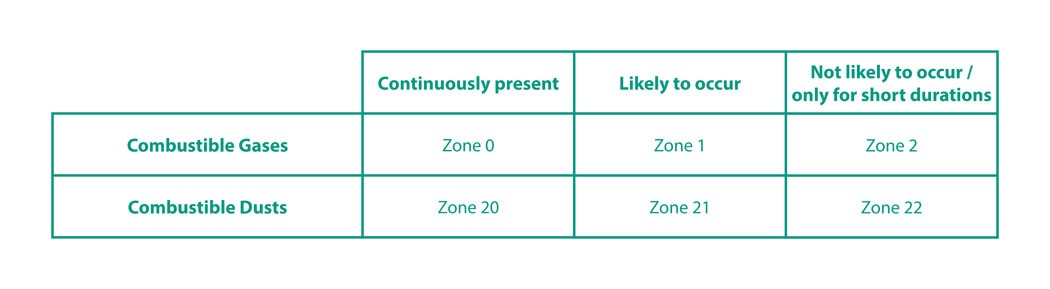
Specifically, formation of explosive atmospheres is to be restricted, ignition sources are to be avoided and the effects of possible explosions are to be minimised. To achieve these objectives, potentially explosive atmospheres (zones) were defined. Different rules which must be followed apply to each zone.
These EU requirements were transposed into German law based on the Industrial Safety and Health Regulations. In Austria, the Directive was implemented by VEXAT.
What is regulated under VEXAT?
“VEXAT” regulates the handling of explosive substances in Austria. The aim of this regulation is to prevent accidents at work caused by such dangerous substances.
The abbreviation of “VEXAT” means “Verordnung über explosionsfähige Atmosphären” [Regulations on Explosive Atmospheres]. This regulation defines the requirements for explosion protection in workplaces. VEXAT is to be used wherever explosive substances are used. These substances include flammable and explosive liquids, gases, vapours or dust.
Important VEXAT provisions include:
- assessment and documentation of explosion hazards at the company;
- employee training and work approvals;
- tests and measurements;
- explosion protection measures.
What relevance do the ATEX and VEXAT directives have for packaging?
These directives have no direct relevance to packaging. However, due to the specifications for operating sites, packaging might be prohibited from building up static charges which could lead to critical discharges.