Food-safe Industrial Packaging

Packaging used in connection with food must be food-compliant. Food packaging must meet certain requirements to ensure that it is not harmful to health.
Which legal regulations for food-compliant packaging exist?
Which legal regulations for food-compliant plastics exist?
What is regulated in the GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice)Regulation no. 2023/2006?
What does “food-safe” mean?
Food-safe means that a material may be used in connection with food. Food-safe materials are not harmful to health and do not change the composition, smell and taste of food.
The term “food-safe” is mostly used colloquially; the official term is “food-compliant” or “food compliance”.
Which legal regulations for food-compliant packaging exist?
All materials which may come into direct contact with food must be tested for food compliance.
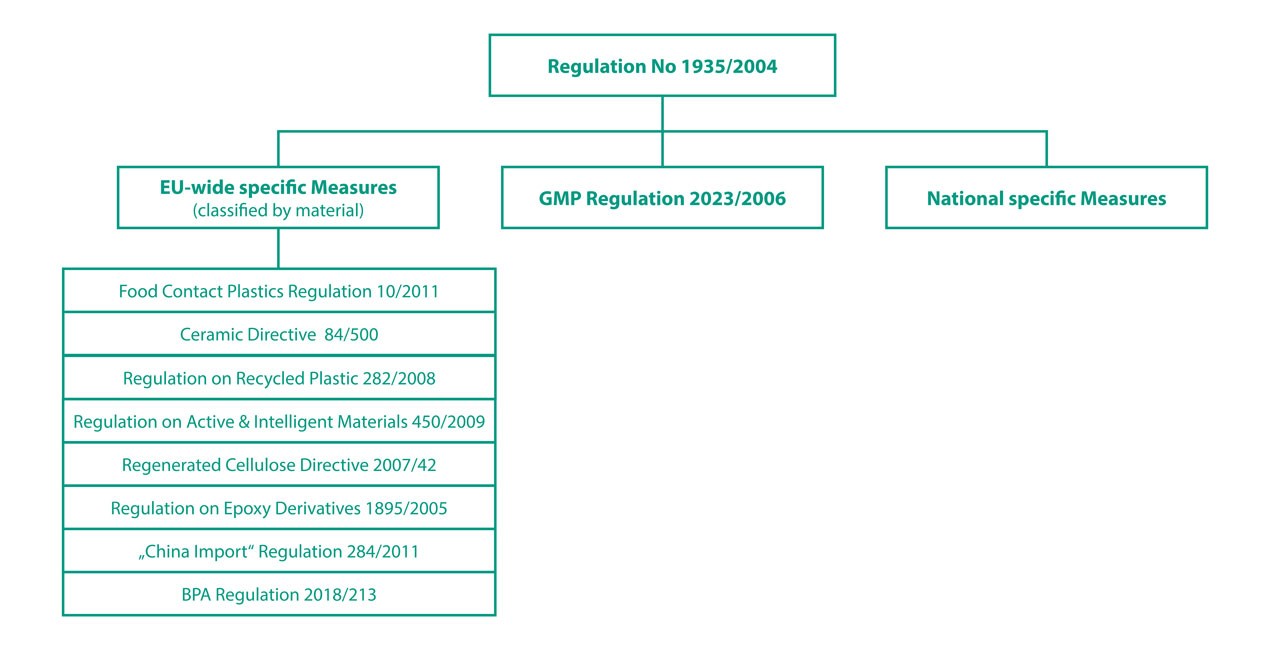
The framework conditions are laid down by the European Union in its Regulation (EC) 1935/2004. The framework regulation for food compliance does not only apply to plastics, but to any packaging material used in the food sector. Paper, cardboard, polystyrene, aluminium, glass etc. must also comply with the regulation.
The framework regulation 1935/2004 regulates the general requirements, labelling, declarations of compliance and traceability of products.
It states that material which comes into contact with food may transfer no or only small quantities of material components to the food.
The transfer of packaging material components to the food is referred to as “migration”. Migration must be on a low level so as to
- not pose a threat to human health;
- not unacceptably change the food composition;
- not affect the smell and taste of the food.
Individual measures on EU level (material-specific regulations), the GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) Regulation no. 2023/2006 and national individual measures are subject to the framework regulation.
Which legal regulations for food-compliant plastics exist?
Apart from the Framework Regulation 1935/2004, there are other individual EU measures for various materials. One of these individual measures is the EU Plastics Regulation no. 10/2011.
This regulates compliance of plastics which come into contact with food. The regulation determines the scope of application, marketability, testing and documentation of the materials.
For a complete version of the EU Plastics Regulation no. 10/2011, please click here >>
How are plastics tested for food compliance? What does “migration” mean in the context of food compliance?
An important part of the Plastics Regulation no. 10/2011 consists in the testing of plastics which come into contact with food.
So-called simulants are used to reproduce the properties of different types of food. There are six food simulants:
- A: Ethanol (10 %)
- B: Acetic acid (3 %)
- C: Ethanol (20 %)
- D1: Ethanol (50 %)
- D2: Vegetable oil
- E: Tenax (solid)
By varying the composition of these simulants, the properties of different types of food can be imitated. Hence, material can be tested for food compliance without using real food.
Food compliance testing always involves the measuring of migration of certain substances into the food (or the food simulant). The test distinguishes between overall migration and specific migration.
Food contact material (FCM)
So-called FCMs are listed in Regulation 10/2011. This material may be used to manufacture food contact material. FCMs are always subject to specific migration limits which must be complied with.
Overall migration limit (OML)
Total migration represents the total amount of chemical substances which migrates or is allowed to migrate into the food. The limit value for this is 10 mg/dm² or 60 mg/kg.
Specific migration limit (SML)
Specific migration indicates the level of migration of defined substances into the food. For all substances mentioned in the Regulation 10/2011, there is a maximum value which must not be exceeded. Specific migration is expressed in milligrams per kilogram of food.
What is regulated in the GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) Regulation no. 2023/2006?
The GMP Regulation no. 2023/2006 determines the requirements for all production areas and stages in the food production, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics sectors. The GMPs serve as a guideline for assuring production process quality. A GMP-compliant quality management system includes:
- qualification of employees;
- equipment testing;
- regular testing of processes;
- quality controls;
- traceability;
- risk management; and
- documentation and internal audits
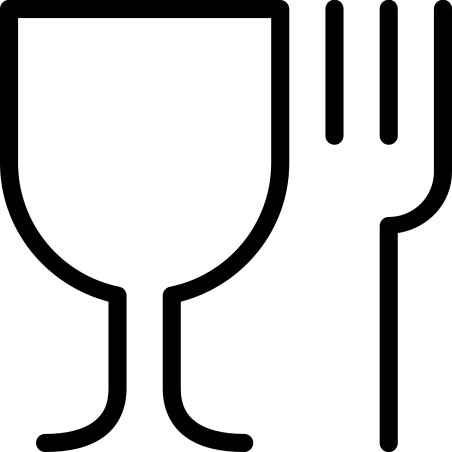
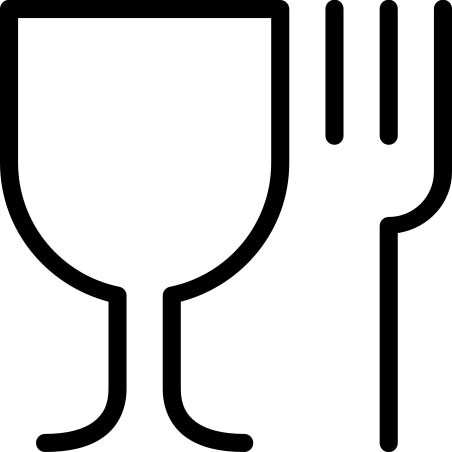
What is the symbol of food compliance?
The well-known symbol showing a glass and a fork is the valid EU food compliance label. This confirms that food may come into contact with the material used without any problems. This symbol is used as an addition if it is unclear that the packaging is suitable for use with food.
The symbol is usually found on the packaging, labels or items themselves.
What is a declaration of compliance and who issues it?
In the declaration of compliance, the manufacturer declares that the product complies with the applicable legal requirements, i.e. that it is in compliance. This declaration is passed on as a document at every stage of the manufacturing process.
The end user receives no declaration of compliance. A consumer based in the EU must be able to rely on the fact that the product he/she purchased meets all the criteria for proper use for food purposes.